The number of industries has been steadily increasing over the last several years, thanks to the rise in worldwide investment in industrial production. This has increased the need for conveyor systems, propelling the market for materials used in conveyor belts. Simply put, conveyor belts move items from one location to another; they are integral to conveyor systems. Depending on their application, various materials, including aramid, metal, and thermoplastic, are utilized for conveyor belts. So, in this article, we will discuss how the conveyor belt moves in airports.
Usually, the belt has three layers—the carcass, the top cover, and the bottom cover—made of any number of materials. Cotton, steel, nylon, polyester, and aramid comprise the carcass layer, which provides linear strength and form. Covers are often constructed from rubber and plastic compounds determined by the belt’s intended purpose. When a high-strength category is needed, conveyor belts are the way to go.
How Does The Conveyor Belt Move In Airports:
Key Players in the Conveyor Belt Industry
The worldwide conveyor belt materials marketplace is predicted to be driven by the need for conveyors, fueled by growth in the food sector and industrial investments. An additional driver anticipated to drive up the need for conveyor belt components during the forecast time frame is the expected global expansion of shopping malls, airports, and industries.
Meanwhile, the hefty price of these materials may put a damper on the demand for conveyor belts. The need for conveyor belt components is also being supplanted by new technology in material handling equipment.

Progress and New Developments in Packaging and Conveyor Systems
Conveyor systems & packaging machinery are constantly developing to keep up with the ever-changing demands of the industrial industry. One example is the rise of robotic automation, which has reduced the demand for human labor while increasing production efficiency and precision.
Software and information analytics improvements have also allowed businesses to monitor and assess how well their packaging and conveyor systems are doing, allowing for constant optimization and improvement.
1. The Factory of the Future
We have entered the fourth industrial revolution, or “Industry 4.0,” to pursue greater efficiency. In this context, new business models are emerging in which sensors and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems are interdependent and cooperate intelligently and effectively.
Using Internet of Things (IoT) technology, the smart factory allows machines to wirelessly interact in real-time with one another and with human operators. Manufacturers can no longer afford to overlook the “Future Factory” since it does more than simply comprehend the tasks at hand; it also learns from them and improves procedures.
Reduced Downtime, Superior Product
One significant advantage of Industry 4.0 is the ability to foresee and avoid unplanned interruptions in the production cycle. It is possible to detect if a machine has problems that can lead to production delays or mistakes by keeping an eye on and understanding everything going on in the operations.
2. Better Work
People worry that robots will supplant humans in the workplace, but that couldn’t be farther from the truth. Some robot activities (such as those of conventional machine tools like CNCs) and their troubleshooting and maintenance still require human operators in the Smart Factory. Although some activities will eventually be automated, robotic assistants will continue to operate in tandem with human operators to do risky or repetitive operations more efficiently and at a lower cost.
3. The Role of Conveyors

In today’s fully automated facilities and applications, conveyors are indispensable. They aid with material transportation, move items from one place to a different one, and are in charge of product orientation and metering. In addition to their many other uses, conveyor-buffer, stage operations, and back-lit conveyors let robotic picking units see better.
Companies are finding that pallet conveyor systems help them make more money. These systems are ideal for a wide range of sectors and operations due to their configuration adaptability.
What Are Airport Baggage Handling Systems?
Conveyors called Baggage Handling Systems (BHSs) are commonplace at airports; they move checked luggage from the counters where passengers check them into the sections where the planes take them. A BHS also carries checked luggage from planes to the places where passengers can get them or to the airside location where they can be transferred to another plane.
An airport’s BHS is vital to the satisfaction of passengers. In addition, it can determine whether an airport can recruit or retain a large airline hub.
The three primary functions of a baggage-handling system are:
- 1 Step: Transport checked bags to the gate for takeoff.
- 2 Step: Transfer checked bags from one plane to another
- 3 Step: Transfer checked bags to the baggage claim area after arrival.
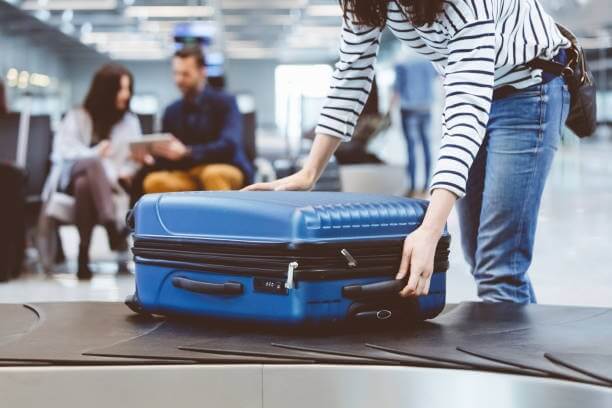

A good baggage-handling system may be measured simply: Are suitcases capable of traveling at the same speed as passengers? If luggage takes longer to move, passengers will be irritated waiting for their bags, or their bags won’t make it to their connecting flights in time. Also, if the luggage moves at a high enough speed, it could make it on the plane, but the people might not.
Because of its major role for United Airlines; Terminal B at Denver International Airport is the most automated of the airport’s terminals. This method uses advanced technology to practically automate the transfer of checked bags from the counter to the departure gate:
- Unmanned carts powered by linear induction motors attached to the rails may load and unload bags without stopping—they are called destination-coded vehicles (DCVs).
- Separators and sorting devices installed on conveyors direct the bags to the exit in an automated fashion.
Baggage handling systems (BHSs) primarily transfer bags from one area of the airport to another, but they also perform ancillary tasks to ensure that bags arrive at their designated destinations.
A BHS’s capabilities extend beyond simple sorting to include:
- Identifying luggage obstructions
- Controlling volume (to prevent system overloads)
- Load balancing (to ensure that all systems receive the same amount of bags)
- Keeping track of bags
- Tracking of bags
In the end: Conveyor Belt Move In Airports
In conclusion, the smooth incorporation of conveyors into the transportation sector; from airports to factories, is indicative of the rapid development of contemporary transportation networks. Conveyors have improved operational procedures and passenger experiences due to their efficiency and dependability; which has changed the movement of commodities and people. Conveyors have become essential parts of the transportation network; simplifying industrial operations and enhancing airport passenger flow and luggage handling.
 Free Web Resources , psd, mockups, & web templates Best WordPress Themes & Best Html Templates
Free Web Resources , psd, mockups, & web templates Best WordPress Themes & Best Html Templates